Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather or vegan leather, is a popular and viable alternative to genuine leather. With its improved durability, versatility, and eco-friendly advantages, faux leather has gained significant traction in various industries, including fashion, upholstery, automotive, and accessories. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of faux leather, detailing its composition, manufacturing processes, benefits, and considerations for potential buyers. 1. Composition and Manufacturing: Faux leather is typically made from a combination of various materials, such as polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and a fabric backing. PU leather is the most common type and is favored for its soft and supple texture, resembling genuine leather. PVC leather, on the other hand, is known for its durability and resistance to water and stains. These materials are often combined with fabric backing to provide strength and support. The manufacturing process of faux leather involves coating a fabric backing with a layer of polymer, which is then embossed, textured, and finished to resemble genuine leather. The result is a versatile and aesthetically pleasing material that imitates the look and feel of real leather. 2. Benefits of Faux Leather: a. Sustainability: One of the significant advantages of faux leather is its sustainability. Unlike genuine leather, which relies on animal hides, faux leather is animal-free and cruelty-free.
leather
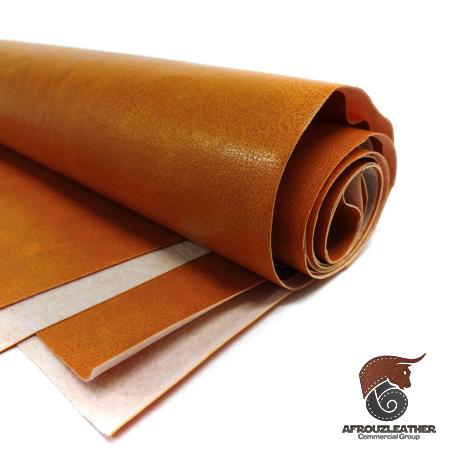 This makes it an ethical and responsible choice for consumers concerned about animal welfare. b. Affordability: Faux leather is typically more affordable than genuine leather, making it accessible to a wider range of consumers. Its lower price point does not compromise on quality, as modern manufacturing techniques allow for high-quality synthetic leather that rivals the look and feel of genuine leather. c. Durability: Faux leather is known for its durability and resistance to wear and tear. It is highly resilient to scratches, fading, and cracking, making it suitable for long-term use in upholstery, fashion accessories, and automotive applications. When properly cared for, faux leather can maintain its appearance for an extended period. d. Versatility: Faux leather offers a wide range of design and color options, allowing for customization and versatility in various applications. It can be embossed, textured, or dyed to resemble different types of genuine leather, such as suede or Nappa leather. This flexibility makes it suitable for a diverse range of products, from clothing and handbags to furniture and car interiors. e. Ease of maintenance: Compared to genuine leather, faux leather is relatively low maintenance. It can be easily cleaned with a damp cloth or mild soap, and does not require the same conditioning and treatment as real leather. This makes it a convenient option for individuals with busy lifestyles or those seeking a fuss-free material.
This makes it an ethical and responsible choice for consumers concerned about animal welfare. b. Affordability: Faux leather is typically more affordable than genuine leather, making it accessible to a wider range of consumers. Its lower price point does not compromise on quality, as modern manufacturing techniques allow for high-quality synthetic leather that rivals the look and feel of genuine leather. c. Durability: Faux leather is known for its durability and resistance to wear and tear. It is highly resilient to scratches, fading, and cracking, making it suitable for long-term use in upholstery, fashion accessories, and automotive applications. When properly cared for, faux leather can maintain its appearance for an extended period. d. Versatility: Faux leather offers a wide range of design and color options, allowing for customization and versatility in various applications. It can be embossed, textured, or dyed to resemble different types of genuine leather, such as suede or Nappa leather. This flexibility makes it suitable for a diverse range of products, from clothing and handbags to furniture and car interiors. e. Ease of maintenance: Compared to genuine leather, faux leather is relatively low maintenance. It can be easily cleaned with a damp cloth or mild soap, and does not require the same conditioning and treatment as real leather. This makes it a convenient option for individuals with busy lifestyles or those seeking a fuss-free material.
Specifications of leather
 3. Considerations and Limitations: While faux leather offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider some limitations before making a purchase: a. Breathability: Faux leather lacks the natural breathability of genuine leather. This can make it feel less comfortable to wear for extended periods, especially in warm weather. However, advancements in fabric technology have led to improvements in breathability, reducing this issue to some extent. b. Environmental impact: Although faux leather is often considered more sustainable than genuine leather, its production can still have environmental implications. The use of certain chemicals and polymers during the manufacturing process can contribute to pollution. However, many manufacturers are working towards more eco-friendly production methods, including using water-based coatings and recycled materials. c. Longevity: While faux leather is durable, it may not have the same lifespan as genuine leather. Over time, faux leather can show signs of wear, such as peeling or flaking, particularly if subjected to excessive heat or friction. However, with proper care and maintenance, faux leather can last for several years and provide a satisfactory lifespan. 4. Applications of Faux Leather: Faux leather has found extensive use in various industries: a. Fashion and Apparel: Faux leather is a popular choice for clothing, shoes, and accessories. It offers a cruelty-free alternative for those who prefer not to use animal-based materials while providing a stylish and fashionable look. b. Upholstery and Furniture: Faux leather is commonly used in furniture upholstery due to its durability and affordability.
3. Considerations and Limitations: While faux leather offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider some limitations before making a purchase: a. Breathability: Faux leather lacks the natural breathability of genuine leather. This can make it feel less comfortable to wear for extended periods, especially in warm weather. However, advancements in fabric technology have led to improvements in breathability, reducing this issue to some extent. b. Environmental impact: Although faux leather is often considered more sustainable than genuine leather, its production can still have environmental implications. The use of certain chemicals and polymers during the manufacturing process can contribute to pollution. However, many manufacturers are working towards more eco-friendly production methods, including using water-based coatings and recycled materials. c. Longevity: While faux leather is durable, it may not have the same lifespan as genuine leather. Over time, faux leather can show signs of wear, such as peeling or flaking, particularly if subjected to excessive heat or friction. However, with proper care and maintenance, faux leather can last for several years and provide a satisfactory lifespan. 4. Applications of Faux Leather: Faux leather has found extensive use in various industries: a. Fashion and Apparel: Faux leather is a popular choice for clothing, shoes, and accessories. It offers a cruelty-free alternative for those who prefer not to use animal-based materials while providing a stylish and fashionable look. b. Upholstery and Furniture: Faux leather is commonly used in furniture upholstery due to its durability and affordability.
buy leather
 It can mimic the appearance of genuine leather and withstand the demands of everyday use, making it suitable for both residential and commercial applications. c. Automotive Industry: Faux leather is increasingly being used in automotive interiors. Its durability, ease of maintenance, and ability to mimic the look and feel of genuine leather make it a preferred choice for car seats, steering wheels, and dashboard covers. d. Accessories and Crafts: Faux leather is a versatile material for creating various accessories, including handbags, wallets, belts, and phone cases. Its flexibility, wide range of colors, and ease of customization make it ideal for crafting unique and fashionable items. Conclusion: Faux leather has emerged as a high-quality and sustainable alternative to genuine leather across several industries. With its affordability, durability, versatility, and ease of maintenance, it offers a compelling solution for those seeking ethical and stylish materials. While faux leather may have its limitations, ongoing advancements in manufacturing techniques and environmental practices are continually improving its quality and sustainability. As consumers become more conscious of the impact of their choices, faux leather is likely to continue gaining popularity as an attractive and responsible alternative.
It can mimic the appearance of genuine leather and withstand the demands of everyday use, making it suitable for both residential and commercial applications. c. Automotive Industry: Faux leather is increasingly being used in automotive interiors. Its durability, ease of maintenance, and ability to mimic the look and feel of genuine leather make it a preferred choice for car seats, steering wheels, and dashboard covers. d. Accessories and Crafts: Faux leather is a versatile material for creating various accessories, including handbags, wallets, belts, and phone cases. Its flexibility, wide range of colors, and ease of customization make it ideal for crafting unique and fashionable items. Conclusion: Faux leather has emerged as a high-quality and sustainable alternative to genuine leather across several industries. With its affordability, durability, versatility, and ease of maintenance, it offers a compelling solution for those seeking ethical and stylish materials. While faux leather may have its limitations, ongoing advancements in manufacturing techniques and environmental practices are continually improving its quality and sustainability. As consumers become more conscious of the impact of their choices, faux leather is likely to continue gaining popularity as an attractive and responsible alternative.

Your comment submitted.